Neurobionics, an MIT spinout, is leading neuromodulation technology to treat neurological disorders like Parkinson, epilepsy, and depression.
Backed by investor Steve Jurvetson of Future Ventures, Neurobionics’ bioelectric fibers will transform patient care by offering a less invasive alternative to traditional deep brain stimulation (DBS).
Neuromodulation Technologies
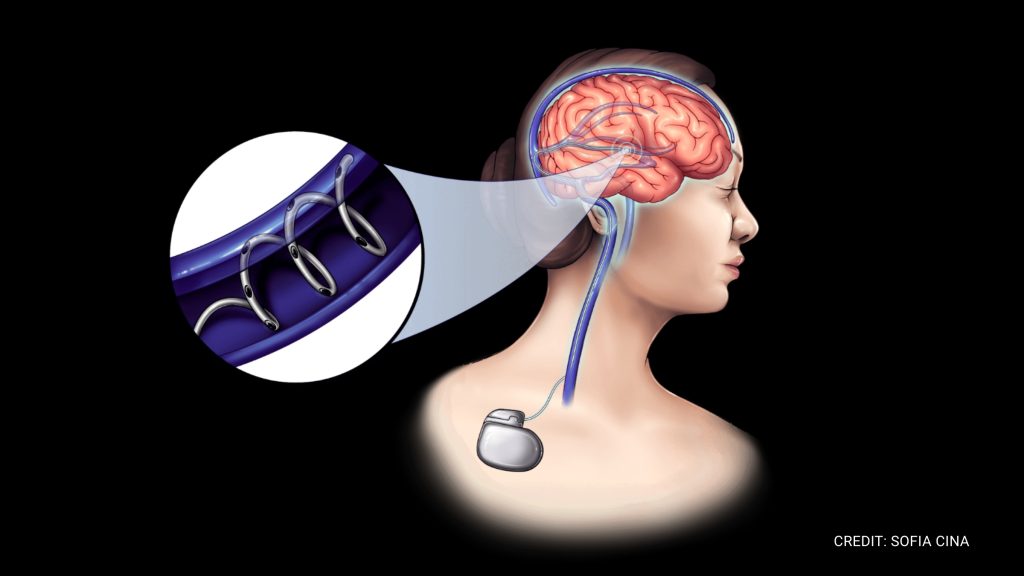
NeuroBionics technology developed the evStim device, a hair-thin bioelectronic fiber delivered through brain blood vessels via a procedure similar to stenting. Once positioned, evSim delivers targeted deep brain neuromodulation simulation therapy by transmitting precise electrical impulses through the vessel wall to specific tissues, according to Neurobionics.
Unlike traditional DBS, which requires drilling into the skull to implant metal electrodes, NeuroBionics’ advanced brain neuromodulation technique uses minimally invasive bioelectric delivered through blood vessels, making the treatment safer with wider accessibility to patients. Less invasive approaches developed by NeuroBionics may make brain neuromodulation therapies accessible for a much larger population.
The neuromodulation technology is powered by a small implantable battery, about the size of an AirPods case, with a lifespan of 5 to 10 years. The battery is already used in other medical devices, such as spinal cord stimulators.
NeuroBionics introduced carbon nanotubes in place of the traditional metals like platinum or iridium oxide. While these metals offer good conductivity, over time, they dissolve causing tissue damage and failure of these devices.
Carbon nanotubes, however, do not have this problem, they are more resistant, less expensive, and make brain imaging and neuromodulation easier because it is compatible with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), they would grant patients a safer and long-lived solution.
According to CEO MJ Antonini, this neuromodulation technology holds back over 10 years of research at MIT, where he co-founded NeuroBionics and secured three patents. Antonini and MIT researcher Nicki Driscoll, now the company’s CTO, recently raised $5 million in funding to continue developing the technology for neuromodulation brain disorders.
Neuromodulation Technology Future
The new brain neuromodulation stimulation technology has potential in the med-tech industry. NeuroBionics sees using these fibers for various medical applications, including drug delivery and treatments for spinal cord and peripheral nervous system disorders.
According to Antonini, the focus now is on conducting more tests and research before being ready to apply on humans by 2030 after Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) approval.
Investors like Steve Jurvetson believe NeuroBionics holds great capability. Although deep brain neuromodulation stimulation is highly effective in cases of Parkinson, epilepsy, and chronic pain, many patients fear the procedure due to risks associated with brain surgery.
The fact that NeuroBionics brought an advanced innovation in medical technology has not helped decrease the worry of patients. For most, the very thought of any neurological procedure stimulates fear in them despite the minimal invasiveness of this technology.
Companies such as NeuroBionics will have to create public awareness and clear concerns to spread trust among their patients. By revealing the neuromodulation technology, proving its safety and benefits, they can help relieve worries and ultimately encourage more patients to consider such high- tech treatments.
Inside Telecom provides you with an extensive list of content covering all aspects of the Tech industry. Keep an eye on our Medtech section to stay informed and updated with our daily articles.