
5G core networks powering digitalization are helping industries cut costs, bring in new sources of revenue, and expand their business offerings. The utility sector is one such vertical, evolving from a labor-intensive organization that provides electricity, water, or gas, to one that uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) and drones to inspect equipment and offers additional services to customers, such as broadband access.
Why Are Utilities Going Cellular?
Utilities have found multiple reasons for investing in LTE or 5G networks. Using a cellular network provides a layer of control not found with Wi-Fi, with added performance, security, and reliability, needed features that offer the mission-critical services necessary for daily living. One survey (1Q21) reports that 69% of utilities asked, “consider real-time communications as a key need driving 5G adoption” and that 38% of utilities asked are “currently using, piloting or testing 5G, with a further 13% planning to implement a solution in the next 12 months.”
Utilities can also offer a Network-as-a-Service, providing ‘last mile’ connectivity for broadband access. Avista Edge and Samsung have successfully trialed an electric meter collar that can be installed in a few minutes and contains all of the 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) networking components that enable high-speed broadband access.
What Applications Will We See?
Utilities will be deploying many intriguing applications with the use of cellular networks. The connection of devices that draw power but now provide no data will offer utilities far more information than they’re getting currently. This ‘smart grid’ will allow consumers to understand their energy usage better and let suppliers improve forecast needs. Using machine learning and AI, utilities will be able to determine where maintenance is needed in time to head off serious problems.
Smart meters will detect leaks sooner, more accurately report usage, and will be helpful for water, gas, and electricity utilities. The Indonesian state-owned electricity provider has worked with Nokia to manage their devices and have constant connections across much of the country, providing real-time power consumption monitoring.
Some utilities are already using drone technology to check for downed or damaged transmission lines, a significant source of wildfires. This is expected to save potentially billions of dollars and improve worker safety. Smart sensors can detect and report leaks rapidly, saving valuable resources.
Vehicles equipped with mobile routers can connect with local devices, gathering information more quickly and accurately than done by hand.
Remote sites such as wind farms or solar arrays will be able to keep in constant contact with utility operating centers, providing real-time information on energy generation.
5G core networks powering digitalization will deliver higher speeds of 5G which will allow improved training and Augmented Reality (AR) assisted maintenance teams to improve repair times.
Barriers to Cellular Uptake
There are reasons why utility companies are hesitant to adopt cellular technologies, including a lack of interest from leadership, who have yet to be convinced of the benefits. Another reason is budgetary constraints and the lack of a solid business plan. Concerns also include a lack of interoperability with existing equipment and a perceived battery life deficiency for connected devices.
Conclusion
One report estimates that 5G-powered smart utilities will add $330 billion to the global GDP by 2030. With the vast capabilities offered to utilities by cellular networks, there is no doubt that we will be seeing significantly changed business models, increased efficiencies, and new functionality in the next few years from our electric, gas, and water suppliers.
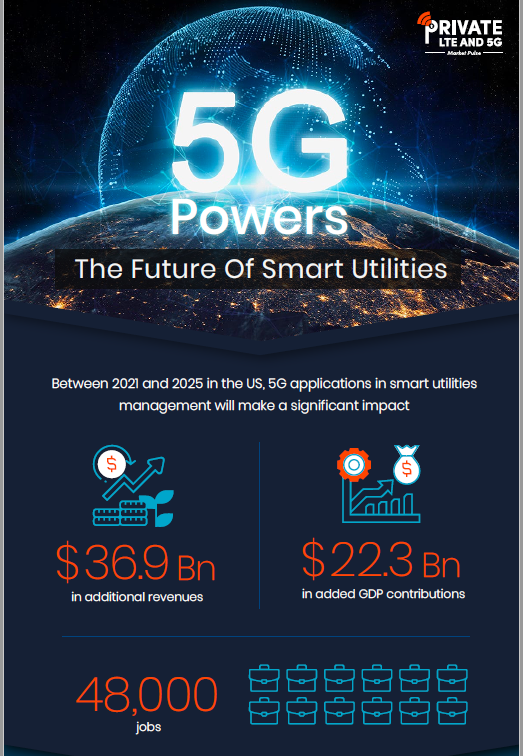
For more information, see infographic here.
Inside Telecom provides you with an extensive list of content covering all aspects of the tech industry. Keep an eye on our Insights sections to stay informed and up-to-date with our daily articles.